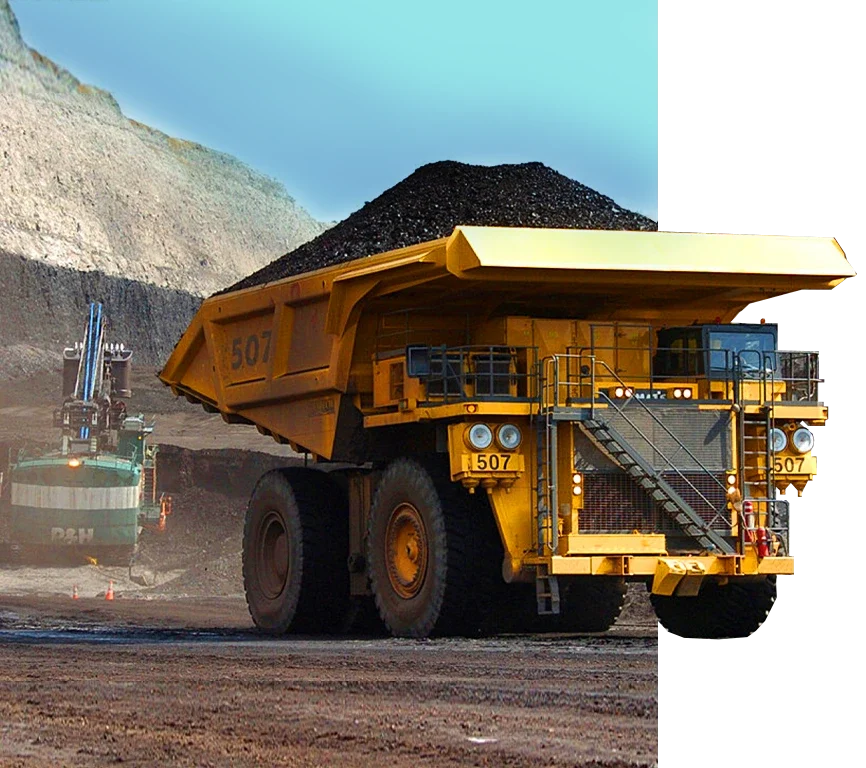
Zaida included 12 former mining concessions comprising exploration and exploitation licenses. This mineralization zone was originally discovered in 1958 in which lead and silver are the highest promising elements for mining. Currently a concession of 3 square kilometers is the target of renewing studies to run mining activities.
The Zaida lead deposit is listed internationally as Sandstone or Red-Bed type deposit. It has, for instance, been listed in the Mineral Deposit Models, USGS Bulletin 1963 and 1987 editions.
The ONHYM formerly known as BRPM (The Moroccan mining research and participation agency) (the equivalent of the USGS) has conducted; exploration studies and technical works on an area of 35 Km2, development studies and built a pilot production plant during the period 1958-1971.
In 1971, BRPM went into a joint venture with other investors to create company called SODIM. SODIM main goal was to extract, process and commercialize the Zaida lead. This deposit was cited, as a Red-Bed or Sandstone deposit, in most of the highly respected international geological records.
In 1984-85 and due to the drastic fall of lead market prices, SODIM decided to close the mine of Zaida.
In 2014 SOCUMA acquired the mining licenses of SODIM as the former owner of 12 mining exploration and exploitation concessions.
After changing the ownership of SOCUMA to MMMC-group in 2023, geological and mineral processing studies as well as market studies are currently being revised.
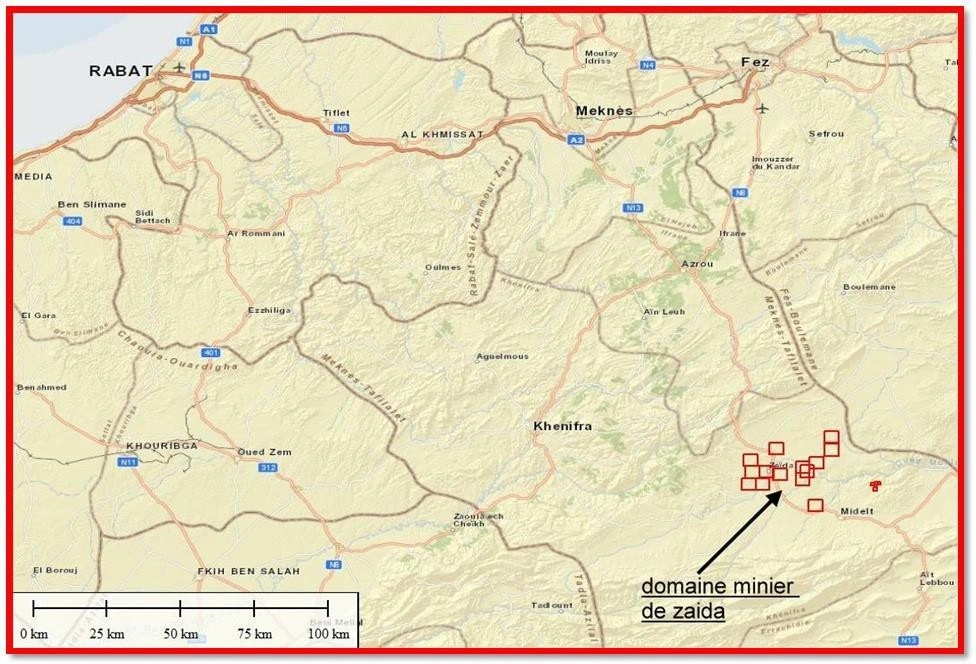
Zaida lead deposit is located on the Moulouya river at the cross section of road N°13 30km NW of the town of Midelt and 150Km SSE of the town of Meknes.
The Zaida deposit is located on the Moulouya basin within the western part of the high plateau. It is a basin surrounded by the high and the middle Atlas. The Hercynian substratum is morphologically composed of two boutonnieres (Fig. 2): Boumia in the SW and Aouli in the East. The deposit is hosted in the detrital Arkose formations Triasic layers.
The Zaida mineralization is composed of 70% Cerusite and 30% Galena. Barite is incidentally present to reach 9% in some of the panels.
Numerous studies were conducted during the 1965-1985 period and provided the following.
• Core drillings; 30,500m
• Destructive drillings; 170,000m
• Geological maps on a scale range; 1/50,000 to 1/200
• Geochemical studies
• Geophysics studies; Electric and gravimetric methods.
The studies cited earlier allowed the illustration of the proved reserves mounting to 18 million tons averaging 3% lead content.